Poliovirus Vaccine IPOL Inactivated: patient information, prescribing information, ingredients, manufacturer, adverse reactions and side effects
Friday, April 07, 2017 by Gregory Van Dyke
http://www.naturalnewsreference.com/2017-04-07-poliovirus-vaccine-ipol-inactivated-patient-information-prescribing-information-ingredients-manufacturer-adverse-reactions-and-side-effects.html
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Typhim Vi safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Typhim Vi.
See full insert sheet at this link at the Natural News Reference website.
IPOL® (Poliovirus Vaccine Inactivated)
Suspension for Intramuscular Injection
Suspension for Subcutaneous Injection
Initial U.S. Approval:
INGREDIENTS AND EXCIPIENTS
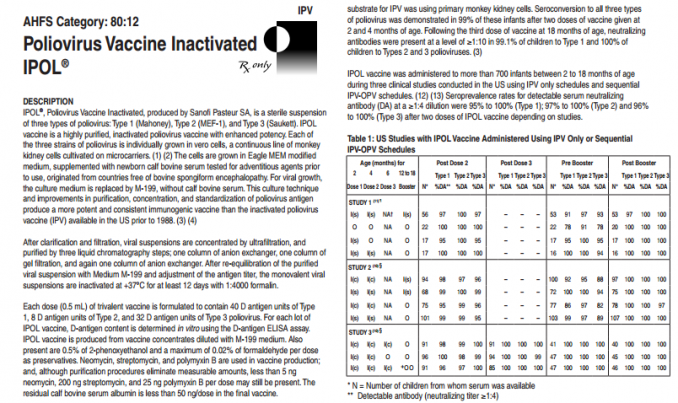
IPOL (inactivated poliomyelitis vaccine), produced by Sanofi Pasteur S.A., is a clear, colourless sterile suspension of three strains of poliovirus: Type 1 (Mahoney), Type 2 (MEF-I) and Type 3 (Saukett). The viruses are grown in cultures of VERO cells, a continuous line of monkey kidney cells, by the microcarrier technique. The viruses are concentrated, purified and made non infectious by inactivation with formaldehyde.
Each sterile 0.5mL immunizing dose of trivalent vaccine is formulated to contain:
Active substance:
| Inactivated Polio virus type 1 (Mahoney) | 40D antigen units |
| Inactivated Polio virus type 2 (MEF-1) | 8D antigen units |
| Inactivated Polio virus type 3 (Saukett) | 32D antigen units |
Excipients
| 2-phenoxyethanol1 | 2 – 3 microlitres |
| Formaldehyde | 2 – 20 mcg |
| Medium 1992 | up to 0.5 mL |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
IPOL is indicated for active immunisation of infants, children and adults for the prevention of poliomyelitis. Recommendations for the use of live and inactivated poliovirus vaccines are described in the national immunisation guidelines.
-
General Recommendations. It is recommended that all infants, unimmunised children and adolescents not previously immunised be vaccinated routinely against paralytic poliomyelitis. IPOL should be offered to patients who have refused OPV, or in whom OPV is contraindicated.
-
IPOL is also indicated for:
– The primary vaccination of immunocompromised individuals of all ages (see PRECAUTIONS), and household contacts of such individuals (when vaccination is indicated)
-
unvaccinated or inadequately vaccinated (*) adults, particularly if at increased risk of exposure to live poliovirus, including:
• Travellers to areas or countries where poliomyelitis is epidemic or endemic;
• Laboratory workers handling specimens which may contain polioviruses;
• Health care workers in close contact with patients who may be excreting polioviruses.
-
(*) Such as those who had not completed a primary series of vaccination or not received a booster dose since infancy.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Primary Immunisation: (see INDICATIONS). Three doses of 0.5 mL each should be administered subcutaneously at intervals of eight weeks.
In infancy the primary schedule is usually integrated with DTPa (Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids and Pertussis Vaccine) immunisation, beginning at 6 to 8 weeks of age.
Booster doses: (see INDICATIONS). All children who have received the initial three doses in infancy should be given a booster dose of 0.5 mL IPOL at 4 years of age.
Adults: (see INDICATIONS). Adults at risk of exposure (see INDICATIONS) who are unvaccinated should receive a primary series of IPOL as outlined above; those with incomplete primary immunisation should receive the remaining doses of the primary series, regardless of the interval since the last dose: those who have previously completed a primary series of poliomyelitis vaccine should receive a single booster dose of 0.5 mL. For those exposed to a continuing risk of infection, a single booster dose is desirable every 10 years.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Vial containing ten 0.5 mL doses
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to neomycin, streptomycin, or polymyxin B. May defer in acute febrile illness.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Have epinephrine injection (1:1000) available. Immunodeficiency. Pregnancy (Cat.C). Nursing mothers.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Local irritation, fever, sleepiness, fussiness, decreased appetite.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Immunosuppressants: may get suboptimal response.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
PREGNANCY
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with IPOL vaccine. It is also not known whether IPOL vaccine can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. IPOL vaccine should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
NURSING MOTHERS
It is not known whether IPOL vaccine is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when IPOL vaccine is administered to a nursing woman.
Revision:
https://www.vaccineshoppe.com/image.cfm?doc_id=5984&image_type=product_pdf
http://naturalnewsreference.com/vaccine-insert-sheets/Poliovirus-Vaccine-IPOL-Inactivated.pdf
Tagged Under: Tags: dosage, ingredients, insert sheet, ipol, Poliovirus Vaccine Inactivated, side effects, usage, warnings