Poliovirus Vaccine Inactivated (Monkey Kidney Cell): patient information, prescribing information, ingredients, manufacturer, adverse reactions and side effects
Thursday, April 06, 2017 by Gregory Van Dyke
http://www.naturalnewsreference.com/2017-04-06-poliovirus-vaccine-inactivated-monkey-kidney-cell-patient-information-prescribing-information-ingredients-manufacturer-adverse-reactions-and-side-effects.html
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Poliovirus Vaccine Inactivated IPOL® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Poliovirus Vaccine Inactivated IPOL® .
See full insert sheet at this link at the Natural News Reference website.
Poliovirus Vaccine Inactivated IPOL®
Suspension for Intramuscular and Subcutaneous Injection
Initial US Approval:
INGREDIENTS AND EXCIPIENTS
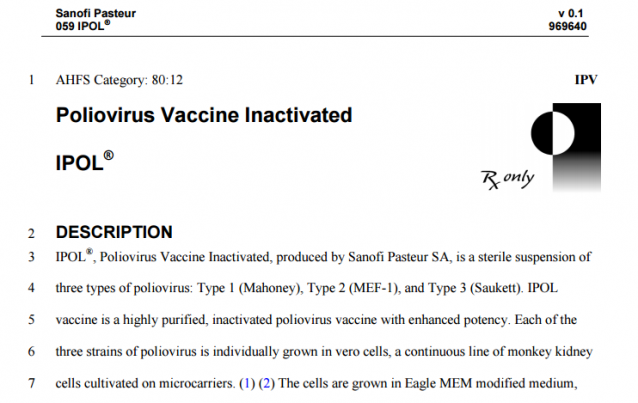
IPOL® 3 , Poliovirus Vaccine Inactivated, produced by Sanofi Pasteur SA, is a sterile suspension of three types of poliovirus: Type 1 (Mahoney), Type 2 (MEF-1), and Type 3 (Saukett). IPOL vaccine is a highly purified, inactivated poliovirus vaccine with enhanced potency. Each of the three strains of poliovirus is individually grown in vero cells, a continuous line of monkey kidney cells cultivated on microcarriers. (1) (2) The cells are grown in Eagle MEM modified medium, supplemented with newborn calf bovine serum tested for adventitious agents prior to use, originated from countries free of bovine spongiform encephalopathy. For viral growth, the culture medium is replaced by M-199, without calf bovine serum. This culture technique and improvements in purification, concentration, and standardization of poliovirus antigen produce a more potent and consistent immunogenic vaccine than the inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) available in the US prior to 1988. (3) (4)
After clarification and filtration, viral suspensions are concentrated by ultrafiltration, and purified by three liquid chromatography steps; one column of anion exchanger, one column of gel filtration, and again one column of anion exchanger. After re-equilibration of the purified viral suspension with Medium M-199 and adjustment of the antigen titer, the monovalent viral suspensions are inactivated at +37°C for at least 12 days with 1:4000 formalin.
Each dose (0.5 mL) of trivalent vaccine is formulated to contain 40 D antigen units of Type 1, 8 D antigen units of Type 2, and 32 D antigen units of Type 3 poliovirus. For each lot of IPOL vaccine, D-antigen content is determined in vitro using the D-antigen ELISA assay. IPOL vaccine is produced from vaccine concentrates diluted with M-199 medium. Also present are 0.5% of 2- phenoxyethanol and a maximum of 0.02% of formaldehyde per dose as preservatives. Neomycin, streptomycin, and polymyxin B are used in vaccine production; and, although purification procedures eliminate measurable amounts, less than 5 ng neomycin, 200 ng streptomycin, and 25 ng polymyxin B per dose may still be present. The residual calf bovine serum albumin is less than 50 ng/dose in the final vaccine.
The vaccine is clear and colorless and should be administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
The vial and vial stopper are not made with natural rubber latex.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
IPOL vaccine is indicated for active immunization of infants (as young as 6 weeks of age), children, and adults for the prevention of poliomyelitis caused by poliovirus Types 1, 2, and 3.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. The vial and its packaging should be inspected prior to use for evidence of leakage or a faulty seal. If evidence of such defects are observed, the vaccine should not be used. Do not remove the vial stopper or the metal seal holding it in place.
After preparation of the injection site, using a suitable sterile needle and aseptic technique, immediately administer IPOL vaccine intramuscularly or subcutaneously. In infants and small children, the mid-lateral aspect of the thigh is the preferred site. In older children and adults, IPOL vaccine should be administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously in the deltoid area. IPOL should not be combined through reconstitution or mixed with any other vaccine.
To help avoid HIV (AIDS), HBV (Hepatitis), and other infectious diseases due to accidental needlesticks, contaminated needles should not be recapped or removed, unless there is no alternative or that such action is required by a specific medical procedure.
Care should be taken to avoid administering the injection into or near blood vessels and nerves. If blood or any suspicious discoloration appears in the syringe, do not inject but discard contents and repeat procedures using a new dose of vaccine administered at a different site.
DO NOT ADMINISTER VACCINE INTRAVENOUSLY.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Vial containing ten 0.5 mL doses
CONTRAINDICATIONS
IPOL vaccine is contraindicated in persons with a history of hypersensitivity to any component of the vaccine, including 2-phenoxyethanol, formaldehyde, neomycin, streptomycin, and polymyxin B.
No further doses should be given if anaphylaxis or anaphylactic shock occurs within 24 hours of administration of one dose of vaccine.
Vaccination of persons with an acute, febrile illness should be deferred until after recovery however, minor illness, such as mild upper respiratory infection, with or without low grade fever, are not reasons for postponing vaccine administration.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Neomycin, streptomycin, polymyxin B, 2-phenoxyethanol, and formaldehyde are used in the production of this vaccine.
Prior to an injection of any vaccine, all known precautions should be taken to prevent adverse reactions. This includes a review of the patient’s history with respect to possible sensitivity to the vaccine or similar vaccines.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In earlier studies with the vaccine grown in primary monkey kidney cells, transient local reactions at the site of injection were observed. (3) Erythema, induration and pain occurred in 3.2%, 1% and 13%, respectively, of vaccinees within 48 hours post-vaccination. Temperatures of ≥39°C (≥102°F) were reported in 38% of vaccinees. Other symptoms included irritability, sleepiness, fussiness, and crying. Because IPV was given in a different site but concurrently with Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids and Pertussis Vaccine Adsorbed (DTP), these systemic reactions could not be attributed to a specific vaccine. However, these systemic reactions were comparable in frequency and severity to that reported for DTP given alone without IPV. (12) Although no causal 2 relationship has been established, deaths have occurred in temporal association after vaccination 3 of infants with IPV. (37)
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Four additional US studies using IPOL vaccine in more than 1,300 infants, (12) between 2 to 18 months of age administered with DTP at the same time at separate sites or combined have demonstrated that local and systemic reactions were similar when DTP was given alone.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
PREGNANCY
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with IPOL vaccine. It is also not known whether IPOL vaccine can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. IPOL vaccine should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
NURSING MOTHERS
It is not known whether IPOL vaccine is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when IPOL vaccine is administered to a nursing woman.
PEDIATRIC USE
SAFETY AND EFFECTIVENESS OF IPOL VACCINE IN INFANTS BELOW SIX WEEKS OF AGE HAVE NOT BEEN ESTABLISHED. (12) (20) (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section.)
In the US, infants receiving two doses of IPV at 2 and 4 months of age, the seroprevalence to all three types of poliovirus was demonstrated in 95% to 100% of these infants after two doses of vaccine. (12) (13)
Revised:
https://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/Vaccines/ApprovedProducts/UCM133479.pdf
http://naturalnewsreference.com/vaccine-insert-sheets/Poliovirus-Vaccine-Inactivated.pdf
Tagged Under: Tags: dosage, ingredients, insert sheet, ipol, Poliovirus Vaccine Inactivated, Poliovirus Vaccine Inactivated IPOL, side effects, usage, warnings